Custom Insert Molding Service
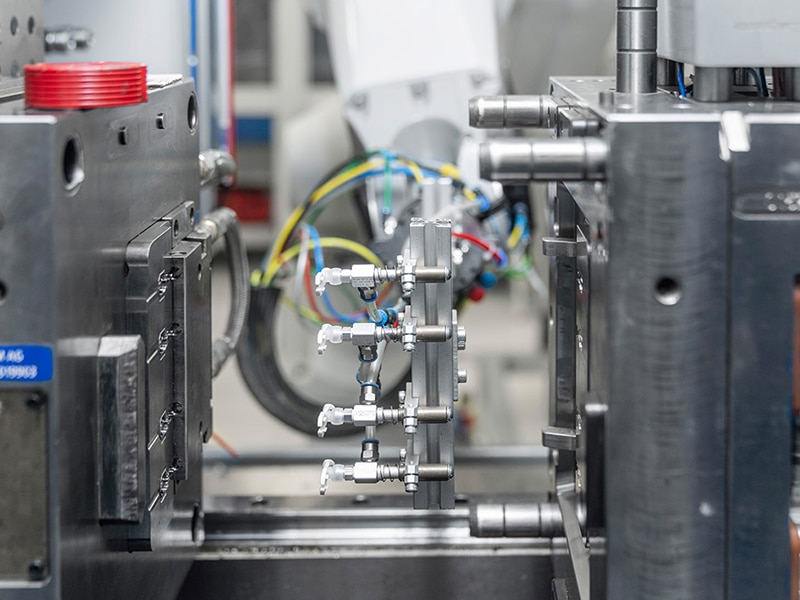
We offer Insert Injection Molding Service that combines metal or other materials into custom molded parts.
Erye is equipped with 30+ sets of advanced molding machines, which allow us to work with various materials, ensuring that the molded parts are not only strong but also optimzied for their intended applications performance.
Our insert molding solution includes:- Molded in metal
- Molded in magnet
- Molded in glass firber
- Molded in ceramic
- Molded in plastic
What is Insert Molding
Insert molding is a manufacturing process to create single, integrated components. The process involves placing a pre-formed insert, particularly metal, into a mold cavity before injecting molten plastic around it. Upon cooling, the insert and plastic form a strongly bonded single part.
This process is distinct from overmolding, which involves mutiple injection steps, whereas insert molding is typically a single-shot process.Insert Injection Molding Benefits
Insert molding is preferred method for manufacturing complex, reliable custom molded parts. Some of the benefits of insert injection molding include:
- Minimize assembly and labor cost
- Reduce size & weight of the part
- Enhanced strength and durablility
- Support flexibility of design
- Improved aesthetic appeal
Insert Molding Service Specifications
| Service | Details |
|---|---|
| Process Materials | Most plastics and rubber, including custom sourcing, see material list below |
| Standard Finishes | SPI and VDI |
| Mold Service | DFM report and mold flow analysis |
| Mold Ownership | Customer owned with regular mold maintenance |
| Mold Cavities | Single or multi-cavities |
| Mold Life | Unlimited (If the mold worn out, Erye will cover the cost for the new set of mold) |
Materials for Insert Injection Molding
ABS
PC
PA
PP
PMMA
POM
LDPE
HDPE
PVC
PTFE
PS
PU
TPE
TPU
TPV
Silicone
EPDM
NR
NBR
CR
SBR
IIR
ABS
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a tough, durable thermoplastic commonly used for products that need to withstand impact and stress, such as automotive components, consumer electronics, and household goods.
The key advantages of ABS injection molding include its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, impact resistance, and ease of customization.

PC
Polycarbonate
PC (Polycarbonate) material is a high-performance plastic known for its excellent strength, optical clarity, and heat resistance. PC is ideal for applications requiring both mechanical durability and visual appeal.
PC injection molding offers advantages such as precise molding of complex shapes in tight tolerances, making it a good choice for producing high-quality, intricate components.

PA
Polyamide
PA (Polyamide), commonly known as Nylon, is a thermoplastic material known for its excellent mechanical properties, such as high strength, toughness, and wear resistance, it also offers good resistance to chemicals, oils, and abrasion.
Nylon injection molding allows for creation of complex, high-precision parts with excellent surface finish and dimensional stability. The reinforced with glass fibers or other additives enhaces it is strength and rigidity.

PP
Polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP) is a commonly used thermoplastic material in injection molding due to its lightweight, durable, and chemical-resistant properties. It is highly resistant to acids, bases, and organic solvents, it also offers low moisture absorption and excellent fatigue resistance.
PP injection molding offers good flow characteristics and high molding efficiency, it can be molded into a wide range of complex shapes with fine details.

PMMA
Polymethyl Methacrylate
PMMA, often referred acrylic or acrylic glass, is a transparent thermoplastic know for its excellent optical clarity, UV stability, and high impact resistance
PMMA injection molding offers good flowability and the ability to create intricate, high-quality parts. It can be molded into complex shapes with precision and a glossy finish.

POM
Polyoxymethylene
POM (Polyoxymethylene), also knows as acetal, is a engineering plastic offers outstanding mechanical porperties, commonly used in injection molding for parts requiring high strength, low friction, and excellent dimenisonal stability.
POM injection molding is a process to produce complex, high-precision component with efficient production cycles.

LDPE
Low-Density Polyethylene
LDPE is a widely used thermoplastic polymer with lightweight, flexible, and durable properties. It has a low density of approximately 0.917 to 0.930 g/cm³, and has a relatively low melting point, making it easy to mold into a variety of shapes.
LDPE injection molding has low-cost and ease to processing which make it a popular choice for high-volume manufacturing.

HDPE
High-Density Polyethylene
HDPE (High-density Polyethylene) is a thermoplastic with high strength-to-density ratio which has excellent chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and can perform well in outdoor envionment.
HDPE injection molding is a highly efficient process for mass production, and able to produce HDPE parts with high stiffness and excellent impact resistance.

PVC
Polyvinyl Chloride
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) comes in two primary forms: rigid and flexible. Rigid PVC is commonly used for pipes, fittings, and profiles, while flexible PVC often used as cables and flooring. PVC is widely used in range of industrial as it is resistant to chemicals, abrasion, and weathering
PVC injection molding parts have excellent dimensional stability and its highly cost-effective.

PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a high-performance plastic that can be used for application that demand superior perforamce in harsh environments.
PTFE injection molding can be challenging due to its high melting point and low flowability. However, PTFE molded components offer excellent durability, low friction, and resistance to corrosion and electrical conductivity.

PS
Polystyrene
PS (Polystyrene) is a rigid, transparent thermoplastic material. Polystyrene is commonly used in applications where transparency is important, such as packaging, disposable cutlery, and cosmetic containers.
Polystyrene injection molding is ideal for high-volume production of simple and lightweight parts. It offers good dimensional stability and can be easily molded into complex designs.

PU
Polyurethane
PU (Polyurethane) has excellent flexibility, durability, and has various hardness levels, which means it can be formulated to be soft or rigid.
Urethane cast molding is typically used for creating prototypes, low-volume production parts, and customized components. PU parts can be highly customized in terms of color, texture, and finish, which can meet specific design requirements.

TPE
Thermoplastic Elastomer
TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) combines the flexibility of rubber with the ease of processing typical of plastics. It is know for its excellent elasticity and weather resitance.
TPE injection molding is a popular choice for producing parts that require soft-touch surfaces, impact resistance, and flexibility, such as seals, grips, and gaskets.

TPU
TPU is a highly flexible and durable material known for its excellent abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and impact resistance. It combines the processing advantages of thermoplastics with the elastic properties of rubber, making it ideal for a wide range of applications, including automotive parts, footwear, medical devices, and electronics. TPU offers good chemical resistance, low-temperature flexibility, and high wear resistance, which makes it suitable for both industrial and consumer products.
TPU is a highly flexible and durable material known for its excellent abrasion resistance, tensile strength, and impact resistance. It combines the processing advantages of thermoplastics with the elastic properties of rubber.
TPU offers good chemical resistance, low-temperature flexibility, and high wear resistance, which makes it suitable for both industrial and consumer products.

TPV
Thermoplastic Vulcanizate
TPV is created by blending vulcanzied rubber particles with a thermoplastic resin, it combines the processing ease of thermoplastics with the rubber-like properties of vulcanized rubber. It is known for its high strength and good abrasion resistance.
TPV injection molding using traditional thermoplastic molding techniques while maintaining the properties of rubber makes it a versatile material for a variety of industries.

Silicone
Silicone Rubber
Silicone rubber has excellent thermal stability, flexibility, and electrical insulation properties. It is also highly resistant to UV, ozone, and weathering. It can withstand a wide temperature range making it ideal for both high and low temperature applications.
Silicone rubber molding is often used to produce seals, gaskets, and custom parts for industries such as automotive, medical, and consumer electronics.

EPDM
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) rubber is commonly used for applications requiring excellent weather, ozone, and UV resistance. It maintains its flexibility and durability even under extreme temperatures.
EPDM compression molding is used to create seals, gaskets, weather strips, and hoses. Its resistance to aging, water, and steam makes it a preferred material for industries such as automotive, construction, and electronics.

NR
Natural Rubber
Natural Rubber (NR) is known for its excellent elasticity, resilience, and abrasion resistance. NR is ideal for applications that require high flexibility and tensile strength. It also offers good resistance to wear, tear, and environmental conditions.
NR compression molding ensures uniformity and consistency in the final product, making it efficient for large-scale production.

NBR
Nitrile Butadiene Rubber
NBR commonly known as nitrile rubber, is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals. NBR is a common used material in automotive, industrial, and oil and gas industires.
NBR compression molding is ideal for manufacturing parts that require tight tolerances and complex shapes.

CR
Chloroprene Rubber
CR, commonly known as Neoprene, is a synthetic rubber with excellent weather, ozone, and aging resistance. CR is especially valuable in applications that require durability in challenging environments, such as automotive, electrical insulation, and marine products.
CR compression molding is often used to produce complex and durable parts, such as gaskets, seals, and protective covers. Neoprene is able to maintain its physical properties over time, even under exposure to environmental stressors.

SBR
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber
SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) is a synthetic rubber commonly used for manufacturing durable and cost-effective parts. It offers excellent resistance to abrasion, aging, and heat, making it ideal for applications requiring toughness and longevity.
SBR compression molding is used to produce components such as seals, gaskets, and automotive parts. Its ease of processing enable efficient production of high-quality molded products that meet strict specifications for performance and durability.

IIR
Isobutylene isoprene rubber
IIR (Butyl Rubber) is a synthetic rubber known for its excellent air and moisture impermeability, making it an ideal choice for sealing applications. It is highly resistant to chemicals, UV light, and oxidation.
In compression molding, IIR butyl rubber is used to create durable, high-quality components like seals, gaskets, and vibration dampeners. The material’s ability to withstand extreme temperatures and its flexibility make it perfect for molding complex shapes with tight tolerances.

Inserts Types for Insert Molding

Metal

Plastic

Magnet

Glass Fiber

Ceramic

Insert Molding Guide
Insert Molding Surface Finishing Standard
| Finishing | Description | Price Range | SPI Grades |
|---|---|---|---|

|
Provides a highly reflective surface, ideal for aesthetic applications such as consumer products. | $$$ | SPI A1, A2, A3 |

|
Offers a moderate sheen, balancing gloss and matte, suitable for parts needing some visual appeal without being overly shiny. | $ | SPI B1, B2, B3 |

|
Features a non-reflextive surface that reduce glare, often used for functional parts where aesthetics are less critical. | $$ | SPI C1, C2, C3 |

|
Enhances grip and durability, commonly applied to functional components to improve handling and reduce wear. | $$$ | SPI D1, D2, D3 |

SPI A: Glossy Finish
Provides a highly reflective surface, ideal for aesthetic applications such as consumer products.
- Price Range: $$$
- SPI Finish Grades: SPI A1, A2, A3

SPI B: Semi-Gloss Finish
Offers a moderate sheen, balancing gloss and matte, suitable for parts needing some visual appeal without being overly shiny.
- Price Range: $
- SPI Finish Grades: SPI B1, B2, B3

SPI C: Matte Finish
Features a non-reflective surface that reduces glare, often used for functional parts where aesthetics are less critical.
- Price Range: $$
- SPI Finish Grades: SPI C1, C2, C3

SPI D: Textured Finish
Enhances grip and durability, commonly applied to functional components to improve handling and reduce wear.
- Price: $$$
- SPI Finish Grades: SPI D1, D2, D3

Advantages of Insert Molding with Us
Enhanced Bonding Strength
Reduced Assembly Time and Costs
Efficient Production
Insert Molding Applications
Insert Molding FAQs
Related Resources of Insert Molding
In the design of plastic parts for injection molding, every feature, dimension, and detail requires
In injection molding, the cooling phase plays a critical role in determining the overall cycle
Dimensional control is a central concern in injection molding. Even when the mold is precisely
When it comes to injection molding, the tooling materials not only affect the quality and
Plastics have become a primary material in modern vehicle manufacturing. The use of automotive plastic
Injection molding cracks are a frequent issue in plastic part production. This defect affects part




















