Thermoforming vs injection molding, both are popular plastic manufacturing techniques. The two processes are good alternatives for one another; however, there are differences between the two processes in terms of the material used, the overall cost, and product design. We’ll have a deeper look at each process and how to choose.
Overview of Thermoforming vs Injection Molding
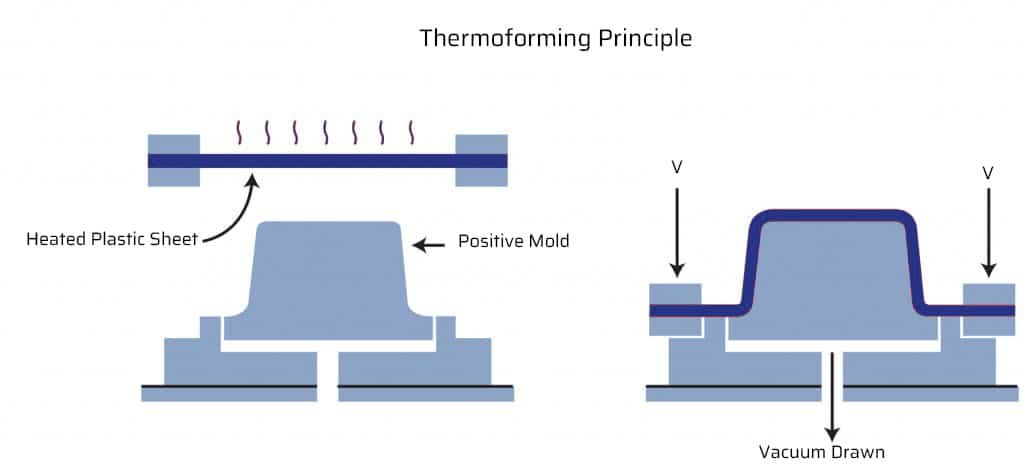
Thermoforming is a manufacturing process that involves heating a plastic sheet until it becomes soft and pliable, then shaping it over a mold using vacuum or pressure. This process is ideal for producing relatively simple parts, including trays, packaging, and large components with low to medium precision.
In contrast, injection molding is a more complex process in which molten plastic is injected into a precisely designed mold cavity under high pressure. This method is highly effective for creating parts with intricate shapes and superior dimensional accuracy, often used in industries like automotive, electronics, and medical devices.
What is the Thermoforming Process?
Thermoforming utilizes a wide variety of thermoplastics, including materials like PVC, ABS, Polycarbonate, and PETG. The process begins with a flat plastic sheet, the sheet is heated until it reaches a pliable state, then placed over a mold. Vacuum or air pressure is applied to the softened plastic, forcing it into the mold’s shape. Once cooled, the formed part is trimmed to remove excess material. This process is fast and cost-effective, especially for low- to medium-volume production runs.
What is the Injection Molding Process?
Unlike thermoforming, injection molding is able to produce a broad range of thermoplastic and thermosetting materials, including polycarbonate, polyethylene, polypropylene, nylon, and various engineering plastics. Injection molding process includes injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic is typically heated to a molten state and then injected into the mold using a hydraulic or electric press. After the material cools and solidifies, the part is ejected from the mold. The process is highly precise, capable of producing complex shapes with tight tolerances and excellent surface finishes. It is well-suited for high-volume production runs.
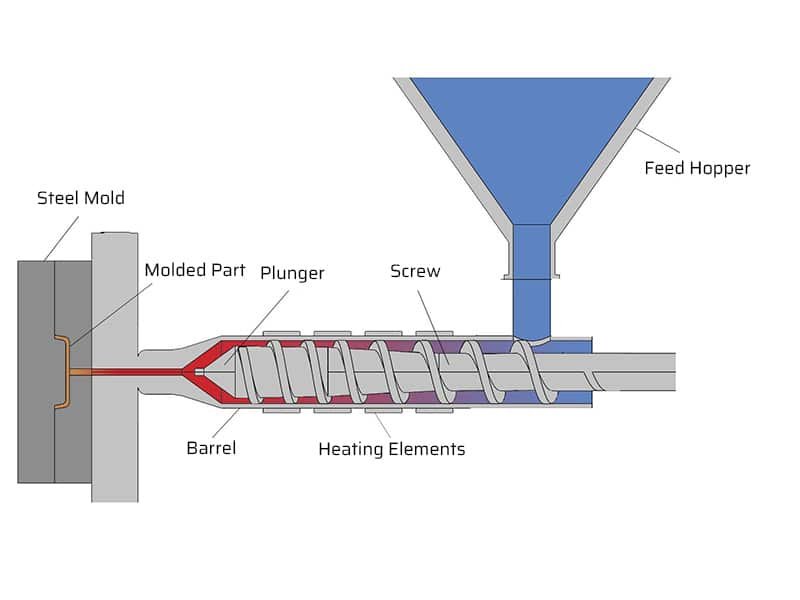
Key Differences Between Thermoforming vs Injection Molding
Thermoforming vs Injection Molding Cost
Thermoforming generally offers lower upfront tooling costs, making it more cost-effective for small to medium production runs. The molds used in thermoforming are simpler and less expensive to produce, which is beneficial for companies with limited budgets or those needing to prototype quickly.
On the other hand, injection molding requires more expensive molds and a higher initial investment, but it becomes more cost-effective at larger production volumes due to its ability to produce high quantities of parts with minimal waste. Learn how much does injection molding cost?
Thermoforming vs Injection Molding: Production Volume and Speed
Thermoforming typically offers faster production times per part, especially for larger and simpler designs. The heating and molding steps are less complex, allowing for quicker cycles.
However, injection molding is far superior for high-volume production, where rapid part ejection and minimal cycle time are crucial. The speed of injection molding increases significantly with larger runs, although the setup time for molds can be longer.
Thermoforming vs Injection Molding: Material Flexibility
Injection molding provides a greater variety of material options, including specialized engineering plastics that thermoforming cannot accommodate. The wide range of materials available for injection molding allows manufacturers to select the best material for the part’s specific functional requirements, such as heat resistance, strength, or electrical properties.
In contrast, thermoforming is more limited to less specialized thermoplastics, although it can still accommodate a diverse array of materials suited for less demanding applications.
Thermoforming vs Injection Molding: Design and Complexity
Injection molding excels in creating parts with intricate geometries, thin walls, and detailed features. The high pressure used in the process allows for precise control over part dimensions, making it ideal for complex designs.
Thermoforming, while capable of producing large parts, is better suited for simpler designs with less intricate detailing. The lack of high pressure in thermoforming limits its ability to handle highly detailed or complex parts.
Thermoforming vs Injection Molding: Tolerance and Precision
Injection molding is renowned for its ability to produce parts with very tight tolerances and superior dimensional accuracy. The mold cavities are engineered to precise specifications, ensuring that each part produced is identical.
Thermoforming, however, has a greater tolerance for variation due to the nature of the process. The vacuum or pressure used in thermoforming can result in slight differences in part thickness and shape, which may not meet the stringent requirements of certain industries.
When to Use Thermoforming vs. Injection Molding
Best Use Cases for Thermoforming: Thin-Walled Parts and Large Sheets
Thermoforming is ideal for creating large parts with simple geometries, especially when thin-walled designs are required. It’s commonly used in packaging, such as clamshell and blister packs, and for automotive interior components like dashboards and door panels. Additionally, thermoforming is well-suited for prototyping due to its low tooling costs and faster turnaround.
Best Use Cases for Injection Molding: High Precision and Complex Shapes
Injection molding is best for high-precision, high-complexity parts that require tight tolerances and intricate features. Its ability to produce a large volume of parts with consistent quality makes it ideal for industries like automotive, electronics, and medical device manufacturing. Injection molding is also the preferred choice for creating parts with multiple cavities, undercuts, or other sophisticated design elements.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Between Thermoformed vs Injection Molding
Design Missteps That Lead to Costly Errors
One common mistake is underestimating the complexity of the design and the limitations of each process. Thermoforming is often chosen for its cost-effectiveness, but designers may not fully account for its limitations in producing intricate shapes or achieving high precision. Similarly, opting for injection molding without fully understanding the tooling and material costs can result in unnecessary expenses.
Underestimating Material Costs and Availability
Material selection is crucial in both processes, and underestimating the cost and availability of certain plastics can lead to production delays or unexpected costs. Both thermoforming and injection molding rely on specific grades of plastic, and sourcing these materials at scale can become a significant factor in the overall cost structure.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Needs
The choice between thermoforming and injection molding depends on a variety of factors, including production volume, part complexity, material requirements, and budget constraints.
Both thermoforming and injection molding offer unique benefits depending on your project’s requirements. Whether you’re looking for the flexibility of thermoforming or the precision of injection molding, we have the expertise and equipment to accommodate your needs. Our engineering team is with you every step of the way, from product design assistance to selecting the best manufacturing method, bulk production, secondary process, and testing. If you’re considering either of these processes for your next product, feel free to reach out for a quote or more information on how we can help bring your ideas to life.