The injection molding cost varies depending on a variety of factors, such as material choice, mold complexity, and production volume. On average, the cost of producing a plastic injection mold can range from $1,000 to $100,000 or more. For example, a simple single cavity-mold for low-volume production might cost between $500 and $5,000, while more complex molds for mass production can exceed $50,000. The cost per part is typically lower for higher production volumes.
In addition to mold costs, there are other associated expenses, such as setup fees, equipment costs, material costs, and labor charges. For small runs, the injection molded part unit cost can range from $1 to $10 or more, depending on the size and complexity of the part. For large runs, this cost can drop significantly, potentially as low as a few cents per part.
Is Injection Molding Expensive?
How much does injection molding cost? Is injection molding expensive? These are the most concerning questions for those who want to start an injection molding project. The cost of injection molding can be expensive, especially when considering the initial costs involved in mold creation and equipment setup. The price of producing an injection mold can range from $1,000 for simple designs to over $100,000 for complex, multi-cavity molds. However, these costs are typically spread across large production runs, that’s why injection molding is more cost-effective for high-volume manufacturing.
For smaller production runs, the costs per part remain relatively high due to the initial investment in the injection mold and machine setup costs for only a few units. On the other hand, when producing thousands or millions of parts, the cost per unit decreases significantly, even as low as a few cents per piece, making injection molding a cost-efficient choice for large-scale production.
Thus, while injection molding may seem costly upfront, it becomes more economical when production volume increases. This can be observed in the Global Injection Molding Market, which has continued to grow over the years. The actual expense depends on factors such as mold complexity, material selection, and the number of parts required. If you’re aiming for large quantities, injection molding is generally a cost-effective solution.
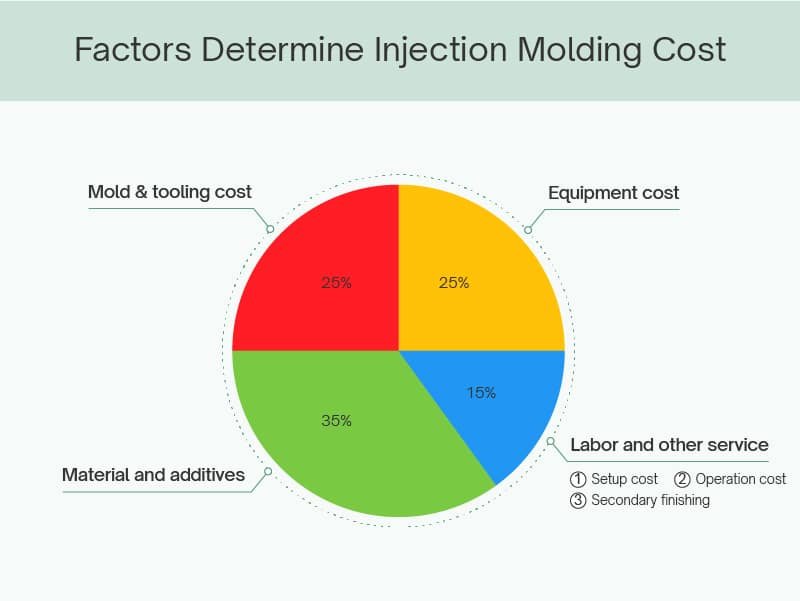
What Are the Factors That Determine Injection Molding Cost
Several major factors affect the overall cost of injection molding, and it is crucial to consider each factor when estimating pricing. Here are the primary elements that contribute to injection molding costs:
- Equipment cost
- Mold & tooling cost
- Material and additives
- Labor and other services
Equipment Cost
The equipment cost is a significant factor in determining the overall injection molding cost. It encompasses several components, including the injection molding machine itself, auxiliary machinery, and associated setup costs. The size, complexity, and capabilities of the machine directly influence the total cost.

The clamping force of the injection molding machine, measured in tons, is directly related to the size and complexity of the mold it can accommodate. Larger machines with higher tonnage capabilities are necessary for producing larger parts or handling molds with more cavities, and this can significantly drive up the cost.
Different types of injection molding machines, such as hydraulic, electric, or hybrid machines, come with varying costs. Hydraulic machines, while less energy-efficient, are typically cheaper upfront compared to electric machines, which have a higher initial cost but offer better precision and energy savings in the long run.
Equipment with automated features such as robotic arms for part removal, automatic material feeders, or in-mold labeling can increase machine cost. However, automatic systems improve production speed and efficiency, leading to reduced labor costs and overall cost per part in high-volume runs.
Mold and Tooling Cost
Injection mold and tooling costs are a major factor that determines the injection molding cost, and it is a large portion of the upfront expenses for an injection molding project. While the mold fee can be high, it is a necessary investment to ensure part accuracy, durability, and long-term production efficiency.
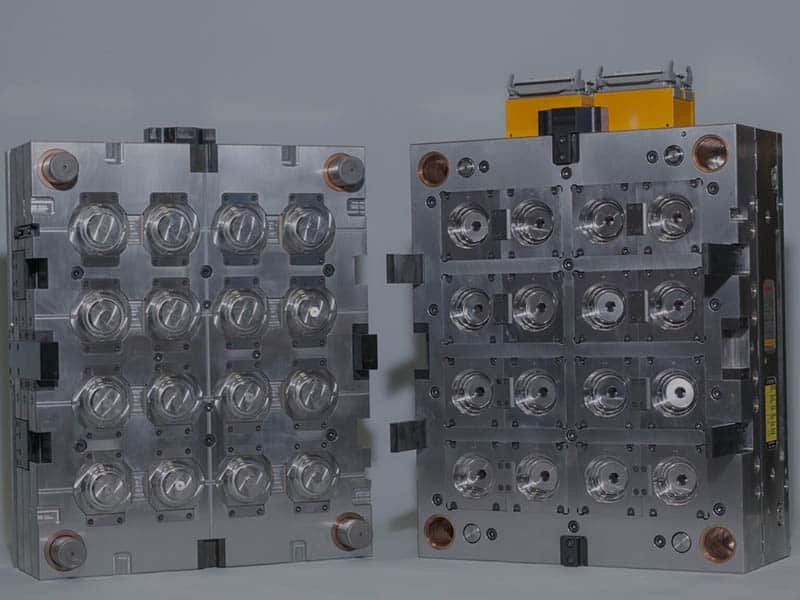
Several key factors influence the tooling and mold cost:
- Mold Design Complexity: The design complexity directly impacts the cost of the mold. More intricate designs, such as those with complex geometries, thin walls, or undercuts, require specialized molds that are more expensive to manufacture. A mold that demands precise, detailed work typically takes longer to design and fabricate, thus increasing the cost.
- Material Used for Mold: The material chosen for the mold itself is a critical factor in determining the cost. For example, steel molds are commonly used for high-volume production runs due to their durability, but at a relatively high cost. Aluminum molds are cheaper and are better suited for low-volume production, but they are easily worn down and may require frequent maintenance.
- Number of Cavities: A multi-cavity mold increases tooling cost due to the added complexity and larger mold base required. Molds with more cavities allow for the production of multiple parts per cycle, improving efficiency in high-volume production runs. However, the more cavities a mold has, the higher the tooling cost.
- Mold Lifetime and Durability: The expected lifetime of the mold also plays a significant role in the overall tooling cost. High-quality, long-lasting molds require higher-quality materials and more advanced manufacturing processes. Molds designed for long-term use, especially in high-volume production, need to withstand high-pressure cycles without wear, driving up the initial investment.
- Mold Maintenance and Repair: Even after the mold is created, ongoing maintenance and repairs can add to the overall cost of tooling. Regular inspections and adjustments are required to keep the mold in optimal condition, and any repairs due to wear or damage can be costly. The more complex the mold, the more expensive the maintenance.
Materials and Additives Cost
The choice of injection molding material and any additional additives can have a significant impact on both the price per part and the overall production budget. Purchasing materials in bulk can help reduce the cost per unit, but smaller manufacturers or prototype runs may face higher material costs due to purchasing in smaller quantities.
The required properties of the material, such as strength, durability, heat resistance, or flexibility, also play a key role in determining costs. For example, materials with specialized features like flame retardancy or high impact resistance tend to be more expensive. A material like polyamide (PA) 66, a high-performance nylon, is costlier due to its superior heat resistance and durability compared to basic materials like polypropylene (PP).

In the injection molding process, material waste is inevitable due to sprue, runners, and flash. This leftover material increases the total consumption and overall cost. While proper mold design and process optimization can help minimize waste, even small increases in material usage—particularly with expensive polymers—can significantly affect the final cost per part.
The cost of materials in injection molding can vary significantly depending on the polymer chosen. As a general reference, here’s an overview of the approximate pricing for different materials:
Common Thermoplastics
These are typically the most affordable materials, with prices ranging from $1 to $4 per kilogram. Examples include:
- Polypropylene (PP)
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
- Polystyrene (PS)
Engineering Plastics
These are more expensive, with prices typically ranging from $4 to $15 per kilogram. Examples include:
- Nylon (PA)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
High-Performance Materials
These are premium materials used in highly demanding applications. Prices for these materials can range from $50 to $100 per kilogram. Examples include:
- Polyetheretherketone (PEEK)
- Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Labor and Other Services
Labor and other service costs are significant contributors to the overall injection molding cost. These expenses encompass various factors such as the time spent on machine setup, the need for secondary processes like trimming or painting, ongoing maintenance and repairs, and the labor involved in the day-to-day operations.
- Setup costs: Include the labor needed to prepare the injection molding machines and molds before production. The setup time depends on the complexity of the mold and machine, with more intricate molds requiring longer preparation times.
- Secondary Finishing: After the initial molding process, parts often require additional finishing work such as trimming, deburring, or painting, depending on the type of finishing required.
- Operational Labor: Despite the reliance on automation, machine operators are still required to monitor the progress of the injection molding process. During production, their wages are considered part of the overall injection molding cost.
- Additional Services: Such as assembly and packaging, costs may vary depending on the part’s complexity, volume, and other requirements.
Injection Molding Cost Estimate
Injection molding cost estimate is critical to any successful project. As a China-based plastic injection molding factory, we manufacture injection molds from draft to completion, and injection molding products price can vary greatly for each project.
Plastic injection molding price can vary based on part design, material, and the specifics of your project. Below is a rough estimate for a small piece of plastic injection molding part, like a small enclosure of an electronic device.
Low-volume production
- Production Volume: 100pcs
- Mold Cost: $100
- Material Cost: $0.5/part
- Labor & Setup: $2.5/part
- Cost per part: $4
Medium-volume production
- Production Volume: 5,000pcs
- Mold Cost: $1500
- Material Cost: $0.5/part
- Labor & Setup: $1.2/part
- Cost per part: $2
High-volume production
- Production Volume: 100,000pcs
- Mold Cost: $5000
- Material Cost: $0.5/part
- Labor & Setup: $0.7/part
- Cost per part: $1.25
How to Reduce Injection Molding Cost
Controlling injection molding costs is a collaborative effort that involves both the factory and the product designer. While the factory plays a pivotal role in most cost-saving measures, product designers can also contribute by making strategic design choices that optimize the production process. Reducing injection molding costs requires practical, actionable strategies that address various factors in the molding process. Below are effective ways to reduce costs.
- Reducing undercuts, as they require complex mold actions (slides, lifters), will significantly increase tooling costs.
- Simplify geometries to avoid sharp corners, deep pockets, and excessive curves.
- Maintain consistent wall thickness to avoid drastic variations, and ensure appropriate wall thickness for strength while minimizing material usage.
- Design the mold properly, which can ensure efficient material flow, minimize defects, and reduce cycle times.
- Increase production output and reduce per-unit cost by incorporating multiple cavities into a single mold.
- Collaborate with experienced molders who can provide valuable design feedback and optimize the manufacturing process.
Our engineer has organized 12 useful tips to reduce injection molding cost. Click and find out more!
Get an Injection Molding Quote For the Cheapest Price and Best Quality
In conclusion, understanding the various factors that influence injection molding costs is essential for making informed decisions and optimizing your production process. Focusing on material choices, mold design, labor costs, and operational efficiency can minimize expenses without compromising on quality.
If you’re looking to get a clearer picture of how much injection molding costs, we’re here to help. Our expert can evaluate and provide the injection mold cost based on your specific requirements. Reach out with ERYE today for a detailed consultation and a quote that aligns with your needs.
FAQs
What is the cost of extrusion vs injection molding?
Extrusion generally has lower initial tooling costs, making it more suitable for simpler shapes and potentially lower production volumes. Injection molding excels at producing complex parts with intricate details, but requires significantly higher upfront investment in tooling.
What is the cost of 3D printing vs injection molding?
3D printing has significantly lower upfront costs due to the elimination of expensive molds. This makes it ideal for low-volume production runs, prototyping, and on-demand manufacturing. Injection molding, while having high initial tooling costs, becomes more cost-effective for high-volume production due to the ability to produce parts much faster and with greater consistency.
As a brief reference, the break-even point for 3D printing versus injection molding typically falls within the range of 500 to 1,000 units, depending heavily on factors like part complexity, material choice, and desired tolerances.