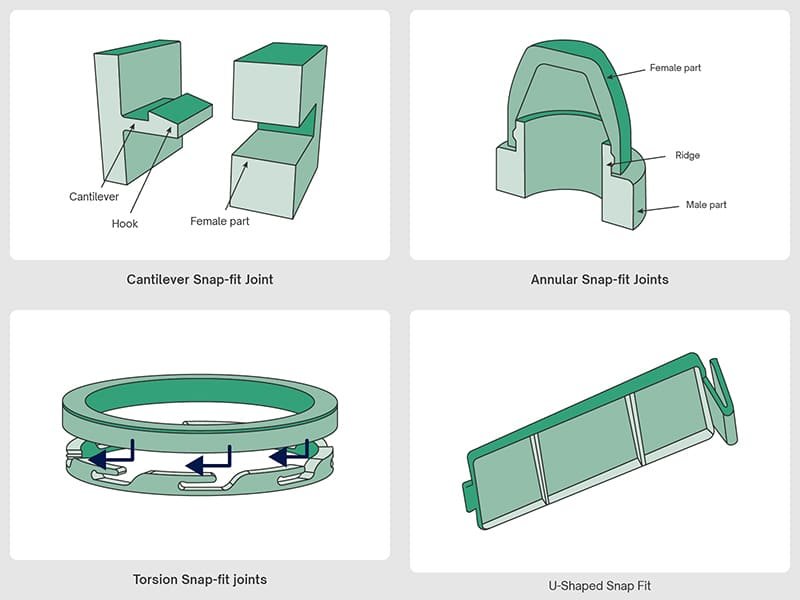
Plastic finishes refer to the surface treatments applied to molded plastic parts, primarily during the molding process, to achieve specific looks and functionalities. Plastic finishes are categorized into four main types: shiny, semi-gloss, matte, and dull. These finishes affect the aesthetic appeal and practical use of plastic products, such as improving grip or durability.
Shiny Finishes
Shiny or high gloss finishes are characterized by their high reflectivity and smoothness, often used for optical parts like plastic mirrors. They are achieved by polishing with diamond powder suspended in oil, ensuring a mirror-like appearance. High-gloss injection molding often requires strict process control, including optimized cooling rates to prevent surface defects like warping or flow lines. Common applications include reflective surfaces in consumer electronics and automotive components.

While glossy finishes improve aesthetics, they also make surfaces more prone to fingerprints, scratches, and glare. To enhance durability, anti-scratch coatings or UV-resistant additives can be applied post-molding.
Semi-gloss Finishes
Semi-gloss finishes provide a smooth surface with a moderate shine—less reflective than glossy finishes but not completely matte. They are achieved using molds with a fine-textured surface or by polishing with controlled grit levels. Techniques like fine abrasive blasting or adjusting the mold cavity texture help fine-tune the level of the sheen without making the surface too reflective.

This finish is ideal for products that need a clean, professional look while keeping maintenance easy, as it helps reduce the visibility of fingerprints and smudges, such as appliance casings.
Matte Finishes
Matte finishes have a low shine and a rougher texture, ideal for internal parts, thermoset, and die-cast components. Matte plastic is produced using chemically etched molds, a polish of fine stone powder or processes like sandblasting, which can result in finishes ranging from satin to dull. These are commonly used in automotive interiors and industrial parts where grip or reduced glare is needed.

Dull Finishes
Dull finishes, often referred to as textured finishes, are the least reflective and provide a rougher surface compared to polished finishes. They are typically used for internal, non-visible components or applications requiring improved grip. These finishes can be achieved through mold texturing techniques such as acid etching, bead blasting, or EDM. These are commonly used for safety-critical parts (e.g., tool handles) or aesthetic designs (e.g., automotive trim panels with wood or polka dot textures).

The Society of Plastics Industry (SPI) has established a widely accepted standard for plastic surface finishes, each category is further subdivided into grades, totaling twelve grades, which allow for precise control over surface appearance and texture.
The following table summarizes these categories and their characteristics:
| Category | Grades | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Shiny | A-1 to A-3 | Smoothest, highly reflective, mirror-like appearance |
| Semi-gloss | B-1 to B-3 | Smooth, moderate shine, less reflective than shiny |
| Matte | C-1 to C-3 | Low shine, rough texture, ranging from satin to dull |
| Dull | D-1 to D-3 | Roughest, least polished, minimal shine |
The right plastic finish depends on how the part will be used, how it should look, and what conditions it will face. Shiny finishes are great for products that need a sleek, polished appearance, while matte and dull finishes help reduce glare and improve grip. Semi-gloss offers a good balance between style and practicality, making it a popular choice for durable parts. It’s also important to consider factors like mold design, material properties, and ease of cleaning.
If you need expert guidance on selecting the best finish for your application, Erye Molding can provide the right solutions to meet your needs. Get in touch with our expert.