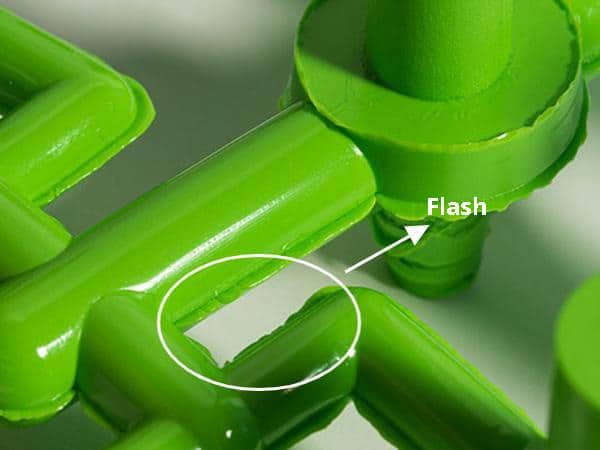
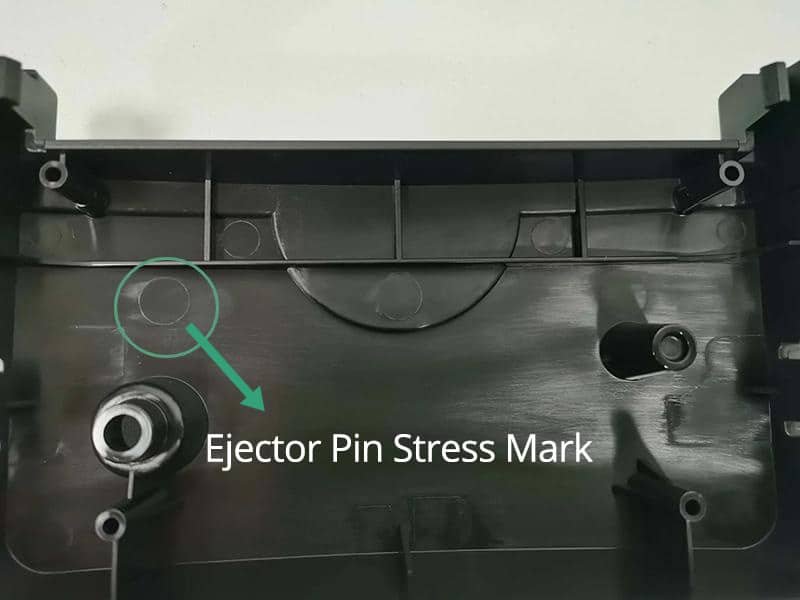
Plastics have become a primary material in modern vehicle manufacturing. The use of automotive plastic material allows manufacturers to produce lighter vehicles compared to those made mostly from metal. Automotive plastic parts appear in interiors, exteriors, and engine areas.
Why is Plastic Material Popular in Modern Vehicle Manufacturing?
Plastics have become the main material for vehicle production due to their practical advantages over traditional materials.- Weight Reduction: Plastics significantly cut vehicle weight, improving fuel economy and extending EV range.
- Cost and Manufacturing Efficiency: Plastic parts are cheaper to make than metal ones; injection molding enables fast, low-waste, large-scale production and simpler assembly.
- Design Flexibility: Plastics allow complex shapes and easy global production while keeping costs competitive.
- Performance Versatility: Plastics can be molded for better aerodynamics and looks; additives enhance durability against UV and chemicals.
- Safety: Plastics absorb impact energy; materials like polypropylene help reduce crash damage.
- Sustainability: Lighter cars emit less CO₂, and recycled plastics (e.g., bumpers) can be reused in new parts.
Common Automotive Plastic Material Types
Several materials dominate automotive plastic parts production.Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) stands out as the most used automotive plastic. It offers good chemical resistance, low density, balanced impact strength, and flexibility. They appear in bumpers, interior trim, battery cases, and air intake ducts.Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) provides impact strength, high toughness, good surface finish, and is easy to paint or plate. ABS handles low temperatures without cracking. It is suitable for dashboards, door panels, interior handles, and wheel covers.Polyurethane PU
Polyurethane (PU) resists abrasion and absorbs vibrations, and provides flexible and rigid forms. They serve dual roles in interiors and exteriors. Flexible PU foams seat cushions and armrests. Rigid PU appears in structural panels.Polyamide (PA / Nylon)
Polyamide (PA) has excellent mechanical strength, heat resistance, and wear properties. They are commonly used in engine covers, intake manifolds, fuel lines, and radiator end tanks.Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC) offers superior impact resistance, optical clarity, and high transparency. They are commonly used in headlamp lenses, sunroofs, and instrument cluster covers.Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
Polybutylene Terephthalate has strong heat and chemical resistance, as well as dimensional stability. They are commonly used in electrical connectors, sensor housings, and fuel system components.Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS)
PPS has exceptional high-temperature performance and chemical inertness. They are commonly used in high-heat engine sensors, fuel rails, and transmission parts.Polyethylene (PE)
PE has high ductility and excellent barrier properties in blow-molded form. They are mostly used in fuel tanks, washer fluid reservoirs, and underbody shields.Key Factors for Material Selection
The plastic material can be used in many automotive parts. The different automotive parts has different requirements about plastic materials.Performance Requirements
Selecting automotive plastic material starts with performance needs. Parts must handle heat, impact, and chemicals. For example, under-hood components require materials with high thermal stability up to 150°C. Strength and stiffness prevent failure during crashes or daily use.Cost
Cost plays a central role. Automotive plastic parts lower production expenses compared to metals. Injection molding allows high-volume output at low per-unit costs.Regulations
Regulations shape choices too. Europe and the US mandate recyclability for plastic auto parts. Materials must meet flammability standards. Environmental rules favor low-emission production processes. Suppliers test for durability under real-world conditions, such as UV exposure and humidity.Applications of Automotive Plastic Material
Plastics are widely used in various parts of the automotive industry.Exterior Automotive Parts
- bumpers
- fenders
- mirror housings
- body side moldings
Interior Automotive Parts
- Instrument panels
- door trims
- center consoles
- seat components
Under-Hood / Powertrain Automotive Parts
- Engine covers
- air ducts
- cooling system reservoirs
- electrical housings