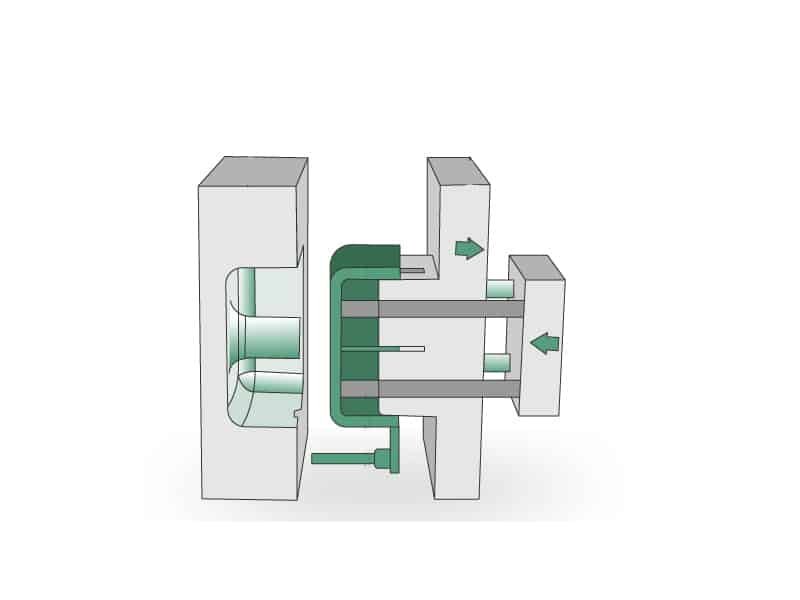
Polypropylene Injection Molding
Whether you need durable components or lightweight designs, our polypropylene injection molding services deliver precision, consistency, and quality to meet your production demands.

Erye Offer Polypropylene Injection Molding Service to Specific to Your Needs!
Polypropylene (PP) is widely used in various industries due to its light weight, durability, and chemical resistance. We offer cost-effective and reliable PP injection molding solutions to meet your high performance and quality standards.
- Free & fast DFM report with optimized designs
- In-housing tooling for fast turnaround with high precision
- Custom material options includes reinforced and impact-modified PP grades
- Advanced molding capabilities from small to large part size, from low-to-high volume production
- Secondary services including assembly, surface finishing, and customization package
Polypropylene Injection Molding Services
| Service | Details |
|---|---|
| Maximum Part Size | 2500mm x 2000mm (98 in. x 78 in.) |
| Recommended Wall Thickness | 0.89 mm and 3.81 mm(0.035 to 0.150 inches) |
| Color Options | Any color according to RAL or Pantone Code |
| Standard Finishes | SPI and VDI |
| Mold Ownership | Customer owned with mold maintenance |
| Mold Life | Unlimited (If the PP mold worn out, Erye will cover the cost of new mold) |
ABS Plastic Molding Design Guidelines
Following are the key design elements that impact both the manufacturing process and the performance of the final ABS molded product.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Wall Thickness | Maintain uniform wall thickness to prevent warping and sink marks. Typical range is 0.5 mm to 5 mm, depending on part size and function. |
| Draft Angles | Include draft angles of 1-2 degrees on vertical surfaces to ensure easy part ejection from the mold. |
| Ribs and Bosses | Design ribs with a thickness of 50-60% of the nominal wall thickness to avoid sink marks; ensure bosses are properly supported (e.g., with ribs) to maintain structural integrity. |
| Radii and Fillets | Use radii and fillets with a minimum radius of 0.5 mm to reduce stress concentrations and improve mold flow during injection process. |
| Shrinkage Considerations | Polypropylene (PP) has a shrinkage rate of 1.0–2.5%, so designs should accommodate dimensional stability. |
| Living Hinges | PP's flexibility allows for living hinges, but the hinge thickness should be 0.25–0.5 mm for durability. |
| Stiffening Features | For large or flat parts, add ribs or other stiffening elements to prevent warping, especially given PP’s higher shrinkage tendencies. |
Start PP Molding Project
Get high-quality PP injection molded parts! Contact with Erye to request a quote!
Key Properies of PP Molding Material
Polypropylene (PP) properties can vary significantly depending on the specific grade (homopolymer, copolymer, etc.) and any additives used. Here's a general overview of key properties with typical data.
| Property | Value/Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.898 - 0.908g/cm³ | Varies slightly between homopolymer and copolymer. |
| Melting Point | Homopolymer: 160 - 165°C; Copolymer: 135 - 159°C | Copolymer has a lower melting point. |
| Tensile Strength (Yield) | 20 - 40 MPa | Range reflects variations in PP types. |
| Elongation at Break | 15 - 700% | Wide range due to different PP formulations. |
| Flexural Modulus | 1.1 - 1.6 GPa | Reflects stiffness; higher for homopolymer. |
| Water Absorption (24 hrs) | <0.01% | PP is highly hydrophobic. |
| Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) | 50-60°C | HDT A (1.8 MPa) |
Key Considerations:
- Homopolymer vs. Copolymer:
- Homopolymer PP is generally stiffer and stronger.
- Copolymer PP offers better impact resistance, especially at low temperatures.
- Additives: Fillers like glass fibers or talc can significantly enhance PP’s mechanical properties.
- Temperature: PP’s properties can change with temperature, and it’s not well-suited for high-temperature applications
Advantages of PP Molding
Cost and Efficiency
PP is relatively inexpensive compared to many engineering plastics, it is an economical option for mass production.
Low Density & Lightweight
One of the lowest densities among common plastics, PP molding parts are typically lightweight, reducing material weight in applications such as packaging and automobiles.
Good Electrical Insulation
Naturally provides strong resistance to electricity, making it useful for housings and electrical components.
Recyclable
Easy to recycle, which lowers material costs and it is more sustainable and cost-efficient in circular use.
Safe for Food Contact
Many PP grades are certified for direct contact with food and drink, making it common in packaging and kitchenware
Disadvantages of PP Molding
Lower Strength and Stiffness
Compared to engineering plastics like nylon or ABS, PP has relatively low mechanical strength and rigidity.
Poor Heat Resistance
Standard PP softens at relatively low temperatures (around 100–120 °C), which limits its use in high-temperature applications.
Shrinkage and Warpage
PP tends to shrink and warp more than some other plastics, which can complicate precision molding.
Poor Bonding and Painting
Its low surface energy makes it difficult to glue, paint, or print on without surface treatments.
PP Injection Molding Applications

Packaging
- Food containers
- Bottle caps and closures
- Medicine bottles
- Storage boxes and bins
- Cosmetic packaging (lids, jars)

Automotive
- Battery cases
- Interior trim parts (door panels, dashboards)
- Fluid reservoirs (washer fluid, coolant)
- Air ducts and housings
Medical
- Syringe barrels
- Specimen containers
- Medical device housings
- Pipette tips
- Diagnostic test cassettes

Industrial
- Chemical storage tanks
- Battery cases
- Industrial containers
- Pipe fittings
- Material handling trays
Additonal Options for Polypropylene Parts

Case Study
Case Study of PP Injection Molding Car Parts
Learn how we helped an automotive client develop a custom injection mold for a car relay box cover. From material selection to mold design, we delivered a complete solution for automotive industry!
Related Polypropylene Molding Resources
Dimensional control is a central concern in injection molding. Even when the mold is precisely
Design for Manufacturing (DFM) is a critical approach that bridges the gap between product design
Demolding is the final step in the injection molding process, where the solidified part is